BIM vs CAD: What’s the Difference and Which One Should You Learn?

- May 18, 2025
- 12:20 am
- 32000+ Comments
Table of Contents
If you are starting a career in architecture, civil engineering, or construction, one of the first questions you will face is: BIM vs CAD – what’s the difference and which one is better to learn?
In this detailed guide, we explain the difference between BIM and CAD, compare their workflows, uses, and career impact, and help you decide which one aligns best with your goals.
This blog is optimized for the long-tail keyword “BIM vs CAD differences”, answering a common question for students and professionals in the AEC industry.
What is CAD?
CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design. It refers to the use of software to create 2D or 3D drawings for engineering and construction.
Key Characteristics of CAD:
- Focuses on drafting geometry (lines, arcs, shapes)
- Widely used for 2D plans and 3D modeling
- No embedded data or smart objects
Common CAD Software:
- AutoCAD
- DraftSight
- MicroStation
- SolidWorks (for mechanical design)

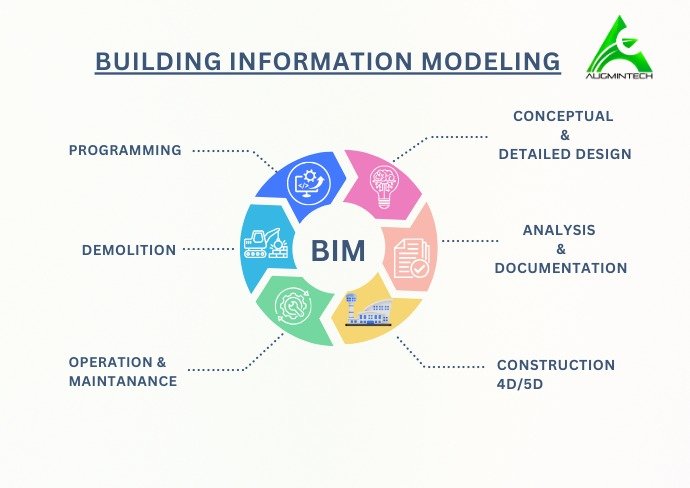
What is BIM?
BIM stands for Building Information Modeling. It is a digital workflow that creates intelligent 3D models containing both geometry and data.
Key Characteristics of BIM:
- Models are data-rich and object-based (walls, doors, ducts, etc.)
- Supports coordination, scheduling, quantity takeoff, and analysis
- Enables cloud collaboration and version control
Common BIM Software:
- Autodesk Revit
- Navisworks
- Archicad
- Bentley OpenBuildings

BIM vs CAD: Key Differences
| Feature | CAD | BIM |
|---|---|---|
| Workflow Type | Drafting-focused | Data-driven modeling |
| Output Format | 2D drawings or 3D models | Coordinated, information-rich models |
| Collaboration | File-based | Cloud-based with real-time sync |
| Clash Detection | Manual checking | Automated in software like Navisworks |
| Quantity Takeoff | Manual or with external tools | Automatic from the model |
| Lifecycle Support | Design only | Design to construction and facility use |
| Industry Standard Usage | Traditional use in 2D drawings | Required in modern AEC projects |
When Should You Use CAD?
- Simple 2D drafting tasks
- Projects with no BIM requirement
- Quick documentation or shop drawings
- Fabrication or manufacturing detailing (especially in mechanical fields)
When Should You Use BIM?
- Projects that require coordination between multiple disciplines (Architecture, MEP, Structure)
- Government or public sector projects that demand BIM compliance
- Complex buildings, infrastructure, and smart city development
- Projects needing 4D (time) and 5D (cost) integration

Which One Should You Learn First?
If you are a student or early-career professional, learning BIM gives you a strategic advantage. While basic CAD knowledge is helpful, the AEC industry is rapidly shifting toward BIM.
Most high-paying jobs in architecture, civil engineering, and MEP now require BIM expertise in tools like Revit, Navisworks, and BIM 360.
🚇 Real-World Example: BIM Replacing CAD in Metro Projects
Industry Shift
In large-scale metro rail and airport infrastructure projects across India and the Middle East, traditional CAD-based workflows are being replaced by integrated BIM processes.
Tools & Collaboration
Leading design firms now utilize Revit for architectural and structural modeling, Navisworks for clash detection and coordination, and Autodesk Construction Cloud (ACC) for cloud-based project collaboration.
Key Outcomes
🚀 Results: Achieved reduced rework, faster government and stakeholder approvals, and significantly improved control over project timelines and quality.
Career Opportunities: BIM vs CAD
| Role Type | CAD Knowledge Needed | BIM Knowledge Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Draftsman | High | Low to Moderate |
| Junior Architect | Medium | High |
| BIM Modeler | Low | High |
| BIM Coordinator/Manager | Low | Very High |
| Project Manager | Medium | High |
Learn BIM with Augmintech’s PG Program
If you want to future-proof your AEC career, the Post Graduate Program in BIM by Augmintech is a great starting point.
Why Choose This Program:
- Covers Revit, Navisworks, BIM 360, Dynamo, and more
- Aligned with ISO 19650 and global standards
- Includes architectural, MEP, and civil projects
- Offers mentorship, certification, and job preparation
Website: augmintech.com
Takeaway
The differences between BIM and CAD are not just technical. They reflect a shift in how buildings and infrastructure are designed, built, and managed. While CAD still has a place in specific tasks, BIM is now essential for most design and construction roles.
If you want to stay competitive in 2025 and beyond, learning BIM should be your priority.


![BIM Management Course Online [2025] – PGP in Architecture for Global BIM Careers](https://augmintech.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/BIM-Management-Course-Online-2025-–-PGP-in-Architecture-for-Global-BIM-Careers.png)