NDT level II certification and Career Opportunities

- October 30, 2023
- 1:37 pm
- 1200+ Comments
Table of Contents
Introduction
Imagine you’re boarding an airplane for your dream vacation, or perhaps you’re driving across a towering suspension bridge. In both cases, your safety is paramount. This assurance is brought to you by the world of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT), a crucial aspect of quality control and safety assurance in various industries. In this blog, we’re embarking on a journey to explore NDT, understand its significance, and particularly dive into the importance of NDT Level ii certification. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clearer picture of how NDT keeps us safe and why NDT Level 2 is a qualification that can transform your career.
What is NDT?
Non-Destructive Testing, or NDT, is like a medical check-up for inanimate objects. It’s the science of inspecting, testing and evaluating materials and components without causing any damage. Think of it as a diagnostic tool for structures, machinery, and even artworks. NDT is vital in industries such as aerospace, manufacturing, oil and gas, and construction.
NDT methods can be as diverse as the materials and structures they inspect. It includes Radiographic Testing (RT), Ultrasonic Testing (UT), Magnetic Particle Testing (MT), Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT), Eddy Current Testing (ET), and Visual Testing (VT). Each method is like a specialized doctor, using its own unique tools and techniques to uncover potential issues.
Importance of NDT Level 2 Qualification
While NDT as a whole is critical, NDT Level 2 qualification stands out. It’s the gold standard of NDT proficiency. Here’s why it’s so important:
Expertise in Multiple Methods: An NDT Level 2 certified professional is skilled in more than one NDT method. This versatility makes them a valuable asset in any industry that requires material inspection and quality control.
Ensuring Safety: NDT Level 2 inspectors play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and reliability of structures and components. Whether it’s an airplane wing or a pipeline, their work is the last line of defense against catastrophic failure.
Career Advancement: Achieving NDT Level 2 qualification opens doors to high-paying and rewarding careers. NDT inspectors are in high demand globally, making it a valuable investment in your professional future.
Quality Control: Level 2 professionals are involved in quality assurance and quality control processes, ensuring that products meet industry standards and regulations
Understanding ASNT NDT Level 2
In the realm of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT), there exists a certification that shines brightly — ASNT NDT Level 2. It’s not just another qualification; it’s a testament to expertise and dedication. This blog aims to unravel the enigma surrounding ASNT NDT Level 2, defining it, distinguishing it from NDT Level 1, and outlining the prerequisites that open the doors to this prestigious certification.
Defining ASNT NDT Level 2
ASNT NDT Level 2 is not just a step up from Level 1; it’s a significant leap. It’s a certification issued by the American Society for Non-Destructive Testing (ASNT) to individuals who have demonstrated a higher level of competence in NDT. When you meet the rigorous requirements and pass the exams, you become an NDT expert.
ASNT NDT Level 2 certifies you to perform, interpret, and evaluate the results of non-destructive tests within a specific NDT method or multiple methods. It’s a powerful acknowledgment of your skills and a seal of approval from one of the most respected NDT organizations globally.
How ASNT NDT Level 2 Differs from NDT Level 1
While both NDT Level 1 and ASNT NDT Level 2 deal with non-destructive testing, the key difference lies in the depth of knowledge and responsibility.
NDT Level 1:
NDT Level 1 certification provides a foundation for a specific NDT method.
Level 1 personnel typically perform the tests and report results under the direct supervision of higher-level personnel, such as Level 2 or Level 3.
They are responsible for following procedures and techniques, but they may not have the authority to make crucial decisions or judgments.
ASNT NDT Level 2:
ASNT NDT Level 2, on the other hand, represents a deeper understanding and a more advanced level of expertise.
Level 2 personnel are authorized to set up and calibrate equipment, perform tests, interpret results, and prepare written instructions.
They have a higher degree of responsibility, and their work plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and reliability of structures and components.
Prerequisites for ASNT NDT Level 2
Becoming an ASNT NDT Level 2 professional is not an overnight endeavor. It requires dedication, experience, and meeting specific prerequisites. The exact requirements may vary depending on the NDT method, but they typically include:
Education: A high school diploma or equivalent is usually the minimum educational requirement. Some methods may require more advanced degrees or specific coursework.
Experience: NDT Level 2 candidates often need to accumulate a minimum of 6 months of hands-on experience in the chosen method.
Training: Completing a formal NDT training program is often mandatory. These programs equip candidates with the knowledge and skills required for Level 2 certification.Click the link below for NDT Level 2 training. https://augmintech.com/courses/ndt-level-2-course/
Examinations: Candidates must pass a series of rigorous written and practical examinations to demonstrate their knowledge and competency.
ASNT NDT Level 2 is more than a certification; it’s a symbol of excellence in non-destructive testing. It represents a deep understanding of NDT methods, a higher level of responsibility, and a commitment to safety and quality. Achieving this certification is a significant accomplishment that can open doors to rewarding career opportunities
NDT Methods Covered in ASNT NDT Level 2 Course
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) methods quietly uphold safety and quality in diverse industries, with NDT Level 2 experts skilfully revealing hidden flaws without causing any harm. This blog will illuminate the array of NDT Level 2 methods, from Radiographic Testing to Visual Testing, showcasing their vital roles in quality control.
Radiographic Testing (RT)
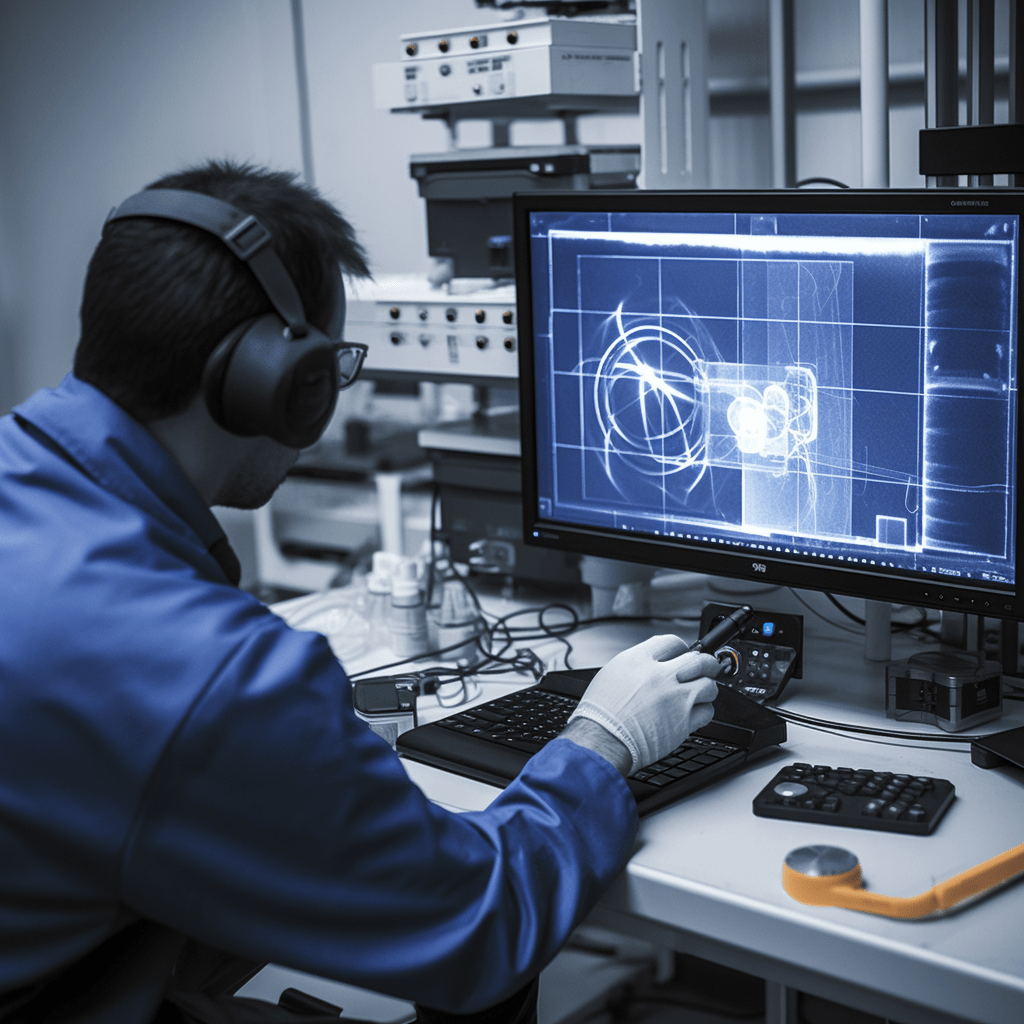
Radiographic Testing, often referred to as RT, is like an X-ray for industrial applications. It involves the use of X-rays or gamma rays to create an image of the internal structure of an object. This method is particularly useful for inspecting welds and detecting internal defects like cracks or voids. The result is a radiograph, much like a medical X-ray, that reveals what the naked eye can’t see.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
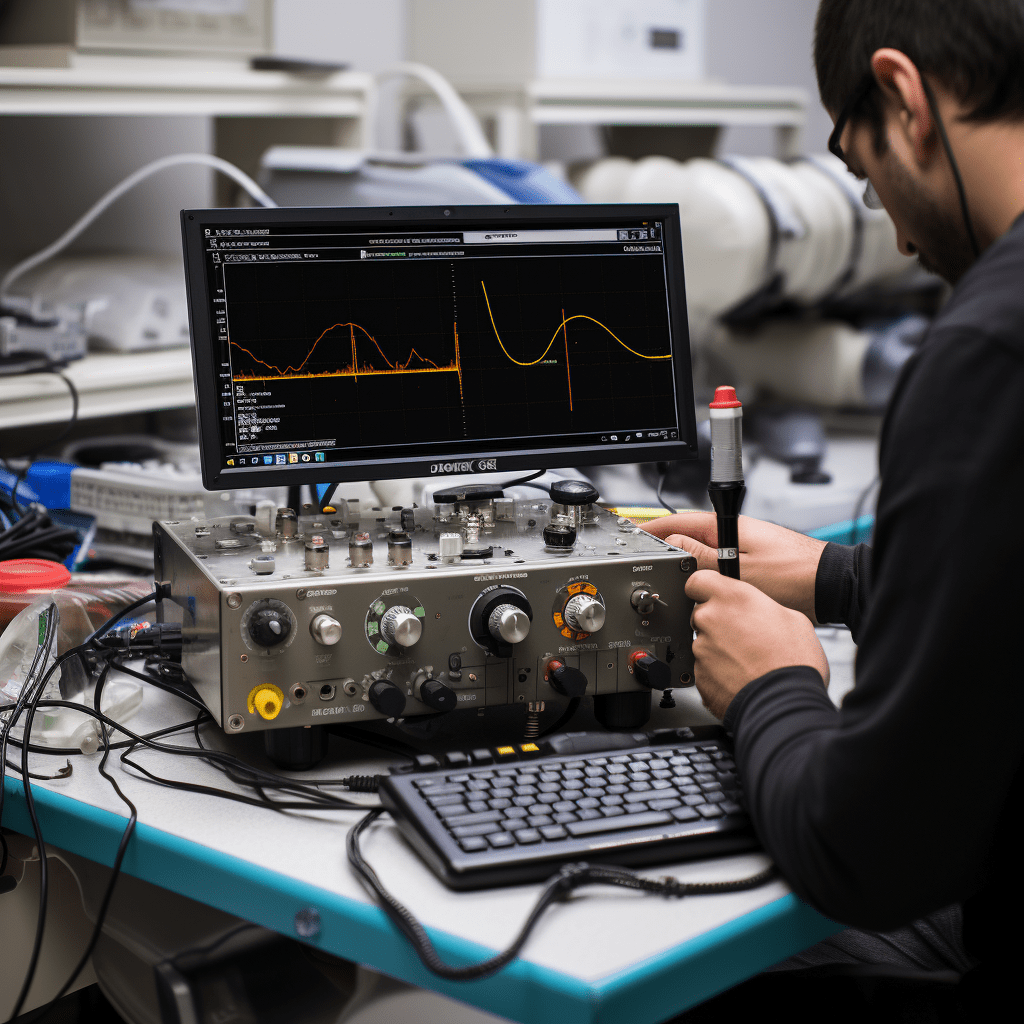
Ultrasonic Testing, or UT, employs high-frequency sound waves to inspect materials and components. A transducer sends sound waves into the material, and their reflections are analyzed to detect anomalies. UT is highly versatile and is used in various industries, including aerospace and manufacturing, to assess thickness, detect cracks, and evaluate the integrity of materials.
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
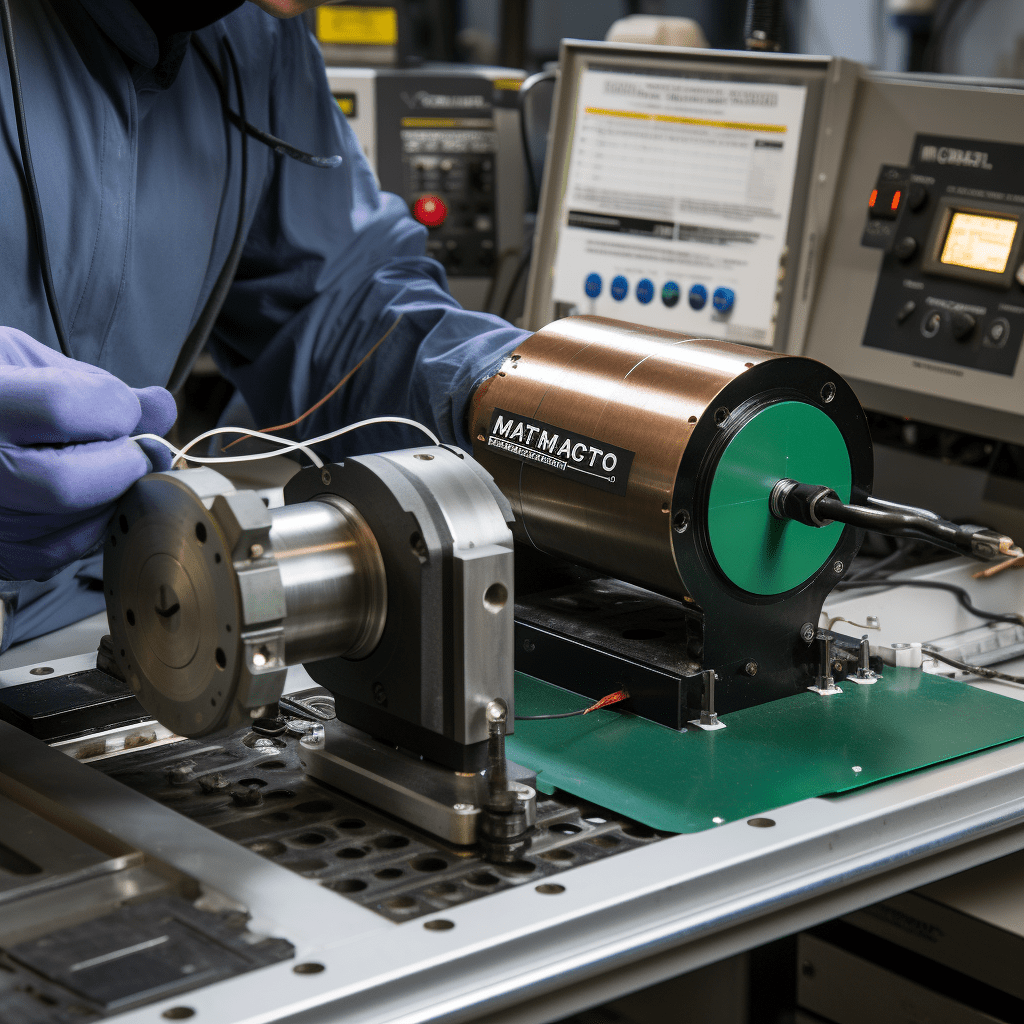
Magnetic Particle Testing, known as MT, is a method for detecting surface and near-surface flaws in ferromagnetic materials. It involves magnetizing the material and applying magnetic particles. When there’s a flaw present, the magnetic particles gather around it, creating a visible indication. MT is a rapid and cost-effective way to find surface defects like cracks and seams.
Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)
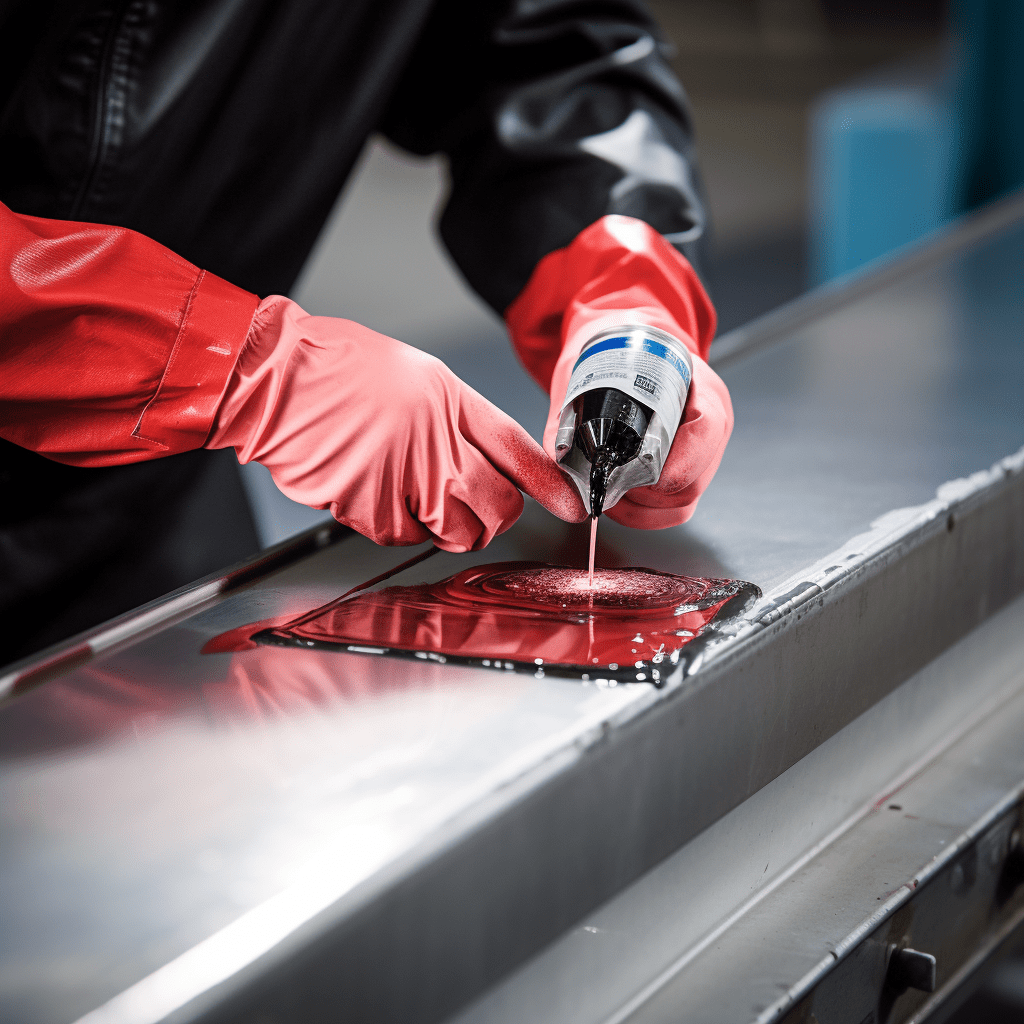

Liquid Penetrant Testing, or PT, is all about finding tiny cracks and defects on the surface of materials. A liquid penetrant is applied to the surface, and it seeps into any openings. After a specific dwell time, the excess penetrant is removed, and a developer is applied. This reveals any defects as vivid, easily visible indications. PT is widely used in the aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
Eddy Current Testing (ET)
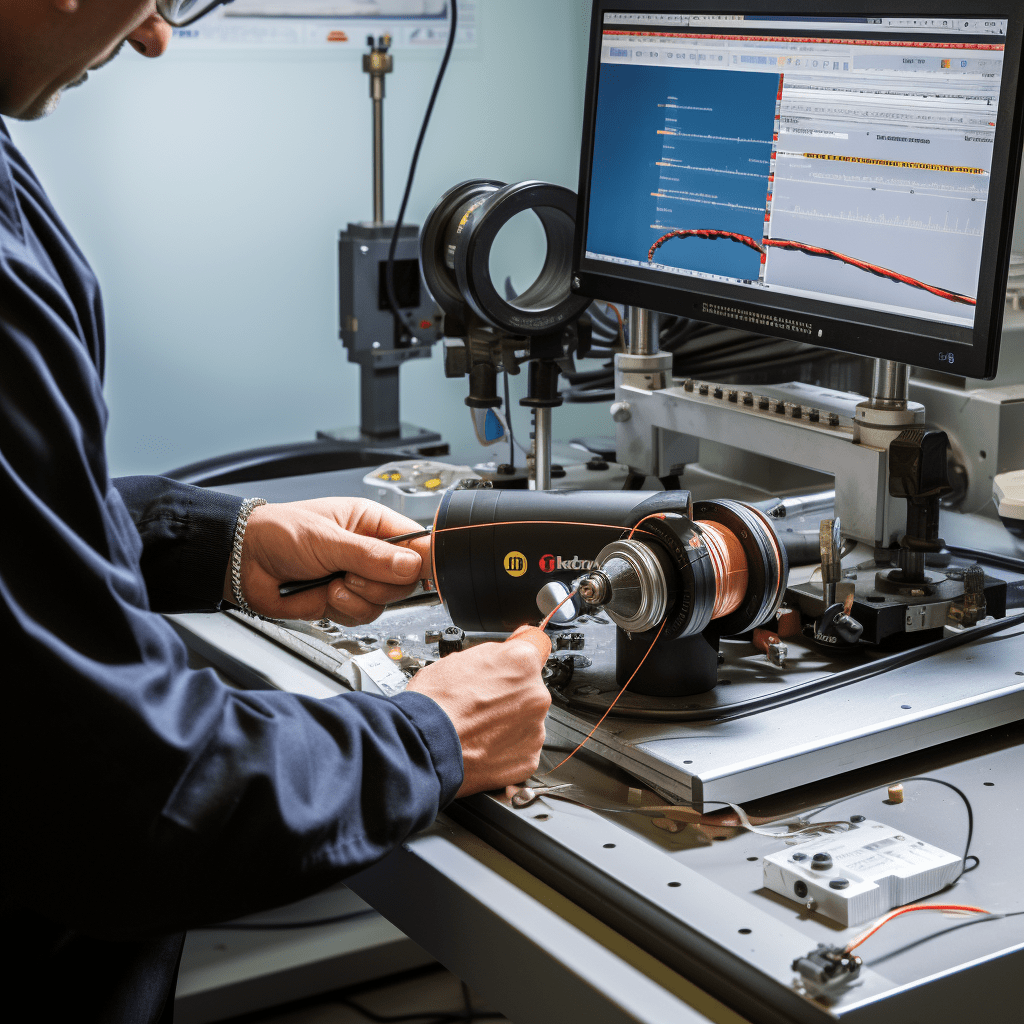
Eddy Current Testing, or ET, is like a magician’s wand when it comes to inspecting conductive materials. It uses electromagnetic induction to create eddy currents within the material. Any changes in the material, such as cracks or corrosion, alter the eddy currents’ behavior, which is detected and analyzed to pinpoint defects. ET is perfect for applications like tube inspection in heat exchangers.
Visual Testing (VT)
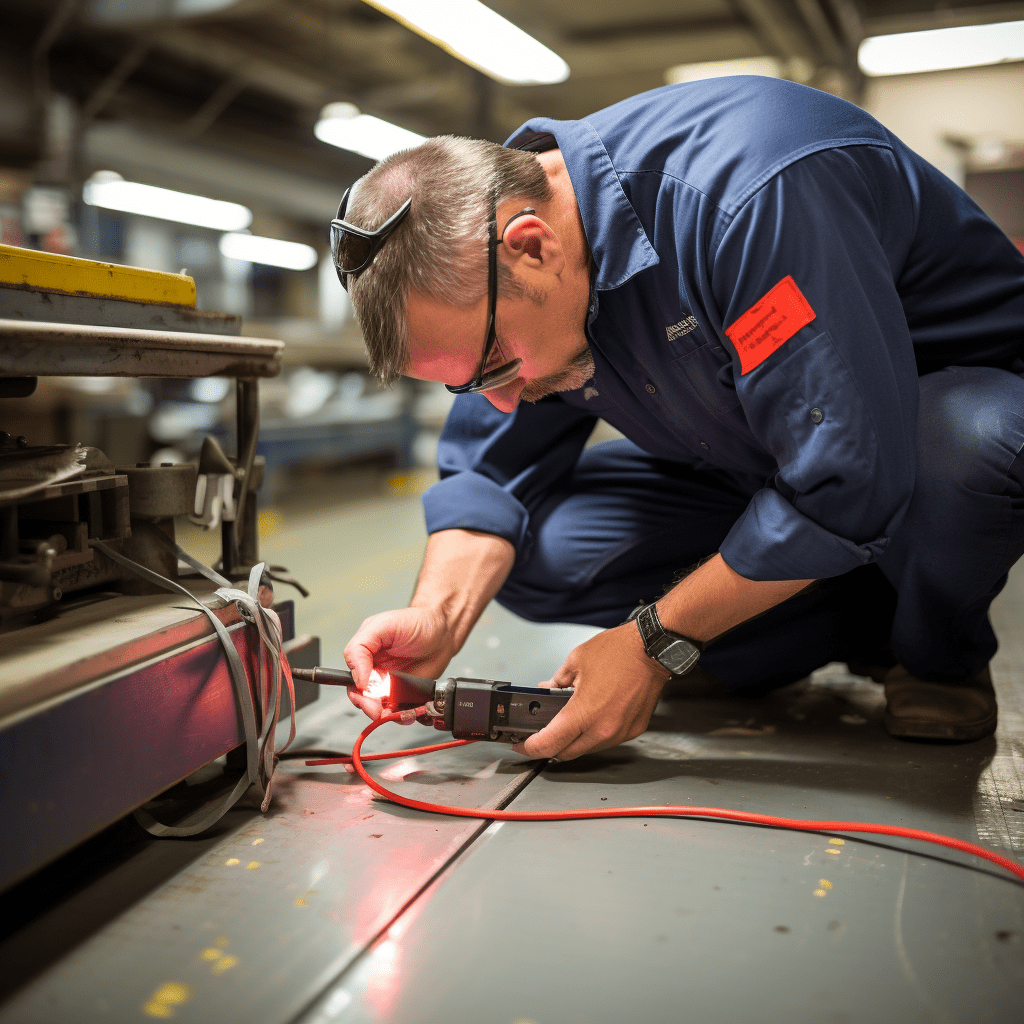

Visual Testing, often referred to as VT, is the most straightforward yet crucial NDT method. It relies on a trained inspector’s keen eyes. Inspectors visually examine the surface of materials, structures, or components for any visible defects, such as cracks, corrosion, or irregularities. VT can be used independently or as a supplementary method alongside other NDT techniques.
In the world of NDT Level 2, these methods are the tools of the trade. Radiographic Testing, Ultrasonic Testing, Magnetic Particle Testing, Liquid Penetrant Testing, Eddy Current Testing, and Visual Testing are the guardians of quality, ensuring that the products we rely on are safe and dependable.
ASNT NDT Level 2 Certification Requirements
Now, we’re going to navigate the path toward ASNT NDT Level 2 certification, dissecting the vital requirements: Training and Education, Experience and Practical Training, and the rigorousExamination and Qualification Process.
Training and Education
The journey to ASNT NDT Level 2 certification begins with the foundation of training and education. This isn’t a quick sprint; it’s more like a well-paced marathon.
Formal Education: A high school diploma or equivalent is often the starting point. However, some NDT methods may require more specialized education or coursework.
Training Programs: Enrolling in a formal NDT training program is crucial. These programs provide comprehensive knowledge and hands-on experience in NDT methods.Click the link below for ASNT NDT Level 2 training and certification. https://augmintech.com/courses/ndt-level-2-course/
Method-Specific Training: Depending on the NDT method, you’ll need method-specific training. For example, if you’re pursuing Ultrasonic Testing (UT) certification, your training should focus on UT techniques and applications.Enroll for free: https://augmintech.com/courses/
ultrasonic-testing-ndt-level-2-course/
Educational Qualifications: In some cases, certain NDT methods may require advanced degrees or additional coursework. This is especially true for methods with a strong scientific or engineering foundation.
Experience and Practical Training

Knowledge is a great asset, but experience is the forge that hones it. ASNT NDT Level 2 certification programs often require candidates to accumulate practical experience:
Hands-On Experience: Depending on the specific NDT method, candidates may need to accumulate a minimum number of hours or years of hands-on experience. This practical training is essential for mastering the techniques and tools of NDT.
Supervised Work: Many certification programs require that hands-on experience be acquired under the supervision of a certified Level 3 professional. This mentorship helps candidates learn and apply NDT skills in real-world scenarios.
Examination and Qualification Process
The ASNT NDT Level 2 certification is earned through a rigorous examination process:
Online Written Examination: Candidates can take a comprehensive written examination online, which assesses their theoretical knowledge of NDT principles, methods, and procedures. This exam may encompass multiple-choice questions and practical problems, all accessible through online platforms.
Virtual Practical Examination: In addition to the written test, candidates can demonstrate their practical skills through a virtual practical examination. This online component evaluates their ability to perform NDT inspections and accurately interpret the results, all within a virtual environment.
Online Qualification: After successfully completing both the online written and virtual practical examinations, candidates can earn the ASNT NDT Level 2 certification. This globally recognized qualification attests to their competence in the field of NDT. The flexibility and accessibility of online testing make it a convenient option for those looking to pursue NDT certification from the comfort of their own environment. To get ASNT NDT level 2 certification, click the link below: https://augmintech.com/courses/ndt-level-2-course/
ASNT NDT Level 2 certification is a journey that requires a combination of formal education, hands-on experience, and rigorous examination. It’s not an easy path, but it’s one that leads to mastery and recognition in the field of NDT. So, if you’re considering this certification, remember that each step brings you closer to becoming an expert in the art and science of Non-Destructive Testing.
Benefits of NDT Level 2 Qualification

Picture yourself at the helm of a career that combines the thrill of discovery, the assurance of safety, and the promise of growth. NDT Level 2 qualification is your passport to such a journey. In this blog, we’ll delve into the remarkable benefits of attaining NDT Level 2 certification. From expanding your career horizons to playing a pivotal role in quality control, and meeting the surging industry demand, this qualification opens doors you never thought possible.
Career Opportunities
Global Recognition: NDT Level 2 certification is like an international seal of approval. It’s recognized worldwide, making your qualifications highly valuable across borders. Whether you’re inspecting pipelines in Alaska or aircraft components in Dubai, your skills remain relevant.
Diverse Industries: The world of NDT knows no boundaries. With NDT Level 2 under your belt, you can explore careers in aviation, construction, manufacturing, oil and gas, and many other sectors. Your expertise is the thread that ties these diverse industries together.
Advancement: NDT Level 2 is not a dead-end; it’s a stepping stone. Once you’ve climbed this certification ladder, you can aim for Level 3, becoming a true authority in your chosen method. Your journey through the NDT ranks is a journey toward continuous improvement and professional growth.
Quality Control and Assurance
Ensuring Safety: NDT Level 2 professionals are the unsung heroes of safety. They meticulously inspect materials and structures, ensuring they meet the highest quality and safety standards. Your work contributes to preventing catastrophic failures in critical industries.
Product Reliability: Your expertise is instrumental in enhancing the reliability of products and structures. Be it the fuselage of an airplane or the welds in a bridge, your inspections provide the assurance that they’ll withstand the test of time.
Minimizing Costs: NDT helps industries identify defects early in the manufacturing or maintenance process. By catching issues before they become critical, you save companies valuable resources, minimize downtime, and ensure that end products are of the highest quality.
Industry Demand
Global Shortage: The NDT industry is experiencing a global shortage of qualified professionals. This translates into a high demand for NDT Level 2-certified individuals. As aging experts retire, a significant void is being created, which only NDT Level 2 professionals can fill.
Attractive Salaries: High demand meets high rewards. NDT Level 2 professionals command competitive salaries, making it one of the most financially rewarding career paths in the world of non-destructive testing.
Steady Growth: The need for NDT professionals is on a steady incline, driven by advancements in technology and the ever-increasing demand for safer, more reliable products and structures. With NDT Level 2, you’re well-positioned to benefit from this growth.
Preparing for NDT Level 2
Stepping into the world of Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Level 2 certification is a journey that promises expertise and countless opportunities. But like any path worth taking, it requires meticulous preparation. In this blog, we’ll be your guide, providing valuable insights on preparing for NDT Level 2. We’ll discuss recommended study materials, offer tips for success, and even provide you with sample questions and answers to boost your confidence and knowledge. Additionally, we’ll highlight a comprehensive NDT Level 2 course by Augmintech, which can serve as an invaluable resource throughout your preparation.
Recommended Study Materials
NDT Textbooks: Start with the fundamentals. NDT textbooks, such as “Introduction to Nondestructive Testing” by Paul McIntire, lay the foundation for your understanding of NDT methods, principles, and applications.
ASNT Learning Materials: The American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT) offers a wide array of study materials, including e-books, reference standards, and online courses, tailored to the NDT Level 2 exams.
Study Guides: NDT study guides, like those from reputable providers such as MISTRAS Group, compile essential information and practice questions to prepare you for the certification process.
Online Resources: Tap into the wealth of online resources, including websites, forums, and YouTube channels that offer video lectures and practical demonstrations. Platforms like the ASNT Learning Center provide a treasure trove of materials.
Augmintech NDT Level 2 Course: Augmintech offers a comprehensive NDT Level 2 course that covers the essential content and provides hands-on training. Check out the Augmintech NDT Level 2 Course here to explore this valuable resource https://augmintech.com/courses/ndt-level-2-course/
Sample Questions and Answers
To give you a taste of what to expect, here are some sample NDT Level 2 certification questions and answers:
1. Radiographic Testing (RT)
Question 1: What is the purpose of an image quality indicator (IQI) in radiographic testing, and how is it used in evaluating radiographs?
Answer: An IQI is used to determine the quality of radiographic images. It contains various thicknesses and materials, allowing technicians to assess the image’s resolution, sensitivity, and contrast. By comparing the image of the IQI to the test object, technicians can ensure the radiograph meets the required quality standards.
2. Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
Question 2: Explain the principle behind ultrasonic testing. How does the velocity of sound in a material relate to flaw detection in UT?
Answer: Ultrasonic testing involves sending high-frequency sound waves into a material. When the sound wave encounters a discontinuity or flaw, it is reflected back to the transducer. The time taken for the sound wave to return is used to calculate the depth of the flaw. The velocity of sound in a material is crucial because it directly affects the accuracy of flaw depth measurements. Different materials have different sound velocities, and this information is used to make precise measurements.
3. Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
Question 3: What is the purpose of a yoke in magnetic particle testing? Explain how it is used in the examination of ferromagnetic materials.
Answer: A yoke is used to induce a magnetic field in ferromagnetic materials. It’s placed on or near the material being inspected. The magnetic field causes magnetic particles to align along the magnetic flux lines. When the material has a flaw, the magnetic field is distorted, causing the magnetic particles to gather at the flaw location, making it visible to the inspector.
4. Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)
Question 4: Describe the steps involved in a liquid penetrant test. What is the purpose of the emulsifier in the process?
Answer: Liquid penetrant testing involves cleaning, applying the penetrant, allowing it to dwell, removing excess penetrant, applying a developer, and inspecting the results. The emulsifier is used to remove excess penetrant from the surface while keeping the penetrant in the discontinuities. It makes the indications more visible during the development phase.
5. Eddy Current Testing (ET)
Question 5: How does eddy current testing work, and what are some common applications in the aerospace industry?
Answer: Eddy current testing uses electromagnetic induction to detect surface and subsurface defects. An alternating current is passed through a coil, generating eddy currents in the material being tested. Discontinuities in the material cause changes in the eddy currents, which are detected and analyzed. In the aerospace industry, ET is used for inspecting aircraft components like engine blades, fasteners, and aluminum structures for cracks, corrosion, and other flaws.
Visual Testing (VT)
Question 6: List three common types of flaws that can be detected through visual testing, and describe their visual characteristics.
Answer: Three common flaws detectable through visual testing are surface cracks (characterized by thin lines or fissures), corrosion (often appearing as pitting or surface degradation), and welding discontinuities (such as incomplete fusion or lack of penetration, visible as irregularities in the weld bead).
Radiographic Testing (RT)
Question 7: What is the primary difference between an X-ray source and a gamma-ray source in radiographic testing? Provide an example of an application where one is preferred over the other.
Answer: The primary difference is the source of radiation. X-ray sources use an X-ray tube to generate X-rays, while gamma-ray sources use radioactive isotopes like Ir-192 or Co-60. In general, gamma-ray sources are preferred in situations where a compact source is needed, such as in pipeline radiography. X-ray sources may be favored for applications that require precise control of radiation intensity, such as in medical radiography.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
Question 8: What is a longitudinal wave, and how is it used in ultrasonic testing?
Answer: A longitudinal wave, also known as a compression wave, consists of vibrations that move parallel to the direction of the wave. In ultrasonic testing, longitudinal waves are commonly used for inspecting materials. They penetrate deep into the material and are suitable for detecting subsurface defects.
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
Question 9: What is the difference between wet and dry magnetic particle testing? When might one method be preferred over the other?
Answer: Wet magnetic particle testing involves suspending magnetic particles in a liquid carrier, while dry magnetic particle testing uses dry particles applied directly to the surface. Wet MT is typically used for testing ferrous materials due to its superior sensitivity and ability to find fine surface cracks. Dry MT is preferred when portability and quick inspections are necessary, such as on-site testing of large structures or equipment.
Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)
Question 10: In liquid penetrant testing, what is the purpose of the dwell time, and how does it affect the sensitivity of the test?
Answer: The dwell time is the period during which the penetrant remains in contact with the surface being tested. It allows the penetrant to seep into any surface cracks or discontinuities. The length of the dwell time affects the sensitivity of the test. Longer dwell times often result in greater sensitivity, as they allow more penetrants to enter small defects, making them more visible during the subsequent inspection and developer stages.
Radiographic Testing (RT)
Question 11: Describe the concept of radiographic density and how it appears on a radiograph.
Answer: Radiographic density is a measure of the degree to which X-rays or gamma rays are absorbed by the material being tested. On a radiograph, denser areas appear darker, while less dense areas appear lighter. This density contrast helps identify defects and variations in the material.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
Question 12: Explain the term “angle beam testing” in ultrasonic testing. When is it commonly used?
Answer: Angle beam testing involves directing the ultrasonic beam into the material at an angle other than 90 degrees. It is typically used to inspect materials with geometrically complex shapes, such as welds or materials with irregular surfaces. Angle beam testing allows for the detection of flaws at different depths within the material.
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
Question 13: What is the purpose of the magnetic particle inspection process known as the “dry method”?
Answer: In the dry magnetic particle inspection method, dry magnetic particles are applied directly to the surface of the material being tested without the use of a liquid carrier. This method is used when portability, quick inspections, or remote testing are necessary, and it is effective for detecting surface cracks in ferrous materials.
Multiple-Choice Questions:
Visual Testing (VT)
Question 14: In visual testing, what type of flaw is MOST likely to be detected by the human eye without additional aids?
A) Subsurface porosity
B) Surface corrosion
C) Weld root penetration
D) Fatigue cracking
Answer: B) Surface corrosion
Radiographic Testing (RT)
Question 15: Which of the following materials is NOT suitable for radiographic testing due to its low density and minimal X-ray absorption?
A) Steel
B) Aluminum
C) Lead
D) Titanium
Answer: D) Titanium
Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)
Question 16: Which step in the liquid penetrant testing process follows the application of the penetrant and precedes the application of the developer?
A) Cleaning the surface
B) Dwell time
C) Removal of excess penetrant
D) Inspection
Answer: C) Removal of excess penetrant
Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
Question 17: Which of the following statements best describes the purpose of a couplant in ultrasonic testing?
A) It prevents the material from overheating during testing.
B) It enhances the visibility of indications on the screen.
C) It allows the ultrasonic waves to travel through the material.
D) It measures the temperature of the material.
Answer: C) It allows the ultrasonic waves to travel through the material.
Eddy Current Testing (ET)
Question 18: Eddy current testing is particularly suitable for inspecting:
A) Non-conductive materials
B) Magnetic materials
C) Ferromagnetic materials
D) Non-ferrous materials
Answer: D) Non-ferrous materials.
NDT Level 2 Training Programs
Online vs. In-Person Training
The debate between online and in-person training is a common one in the modern educational landscape. Both approaches have their merits:
In-Person Training: This traditional method allows you to have face-to-face interactions with instructors, participate in practical exercises, and access physical training facilities. It’s a highly effective way to learn hands-on techniques and ask questions in real-time.
Online Training: The digital age has ushered in a new era of online education. Online NDT Level 2 courses offer flexibility, allowing you to learn at your own pace and in your preferred environment. These programs often include interactive modules, virtual labs, and access to a wealth of resources. Augmintech, for instance, offers an ASNT NDT Level 2 course online, making it accessible to a global audience .To get ASNT NDT level 2 certification, click the link below: https://augmintech.com/courses/ndt-level-2-course/
The choice between online and in-person training depends on your individual preferences and circumstances. Augmintech online course, for instance, brings the benefits of accredited training to your doorstep, allowing you to balance your training with other commitments.
Cost of NDT Level 2 Certification
Augmintech’s offers ASNT NDT Level 2 course and certification at a very affordable cost. You can check the fee here https://augmintech.com/courses/ndt-level-2-course/ The investment is worth the knowledge, skills, and global recognition that you gain.
Additionally, consider the potential return on investment as you embark on a lucrative NDT career.
Investing in your NDT Level 2 certification is an investment in your future. The cost of NDT training programs can vary widely based on factors such as the method you choose, the location of the training centre, and the type of training (online or in-person). However, it’s essential to consider this cost as an investment that can lead to a high-paying and rewarding career. NDT professionals are in high demand, and this demand translates into competitive salaries. Moreover, this certification can open doors to a wide range of industries, from aerospace to oil and gas, each with its unique set of opportunities.
Career Paths After NDT Level 2
In this section, we’ll be your compass, guiding you through the captivating career paths that await after NDT Level 2 certification. From the core roles of an NDT inspector to the pinnacle of NDT expertise in Level 3, and the diverse industries eagerly hiring NDT Level 2 inspectors, we’ll unveil a realm of possibilities.
Inspector Roles
Radiographic Testing (RT) Inspector: As an RT inspector, you’ll be using X-rays or gamma rays to examine materials for defects. Your expertise will be critical in industries like aerospace, construction, and manufacturing.
Ultrasonic Testing (UT) Inspector: UT inspectors rely on sound waves to detect internal flaws in materials. Your keen eye and technical skills are in high demand in fields such as oil and gas, automotive, and nuclear power.
Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) Inspector: MT inspectors use magnetic fields to locate surface and near-surface flaws. Industries such as shipbuilding, railways, and infrastructure rely on your ability to ensure safety and reliability.
Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT) Inspector: PT inspectors identify surface defects through the use of penetrating liquids. This role is crucial in the aerospace, petrochemical, and manufacturing sectors.
Eddy Current Testing (ET) Inspector: ET inspectors use electromagnetic fields to detect cracks, corrosion, and more. Aerospace, electronics, and automotive industries value your ability to keep their products safe and reliable.
Visual Testing (VT) Inspector: VT inspectors are the eyes on the ground, visually examining materials and structures for defects. Virtually every industry, from construction to food processing, benefits from your vigilance.
Roles Beyond Inspection
Quality Control Specialist: Beyond inspection, NDT Level 2 professionals can specialize in quality control. In this role, you’ll ensure that processes and products meet industry standards and regulatory requirements. You’ll be instrumental in maintaining quality throughout production processes.
NDE Technician: Non-Destructive Evaluation (NDE) technicians go beyond inspection by using advanced testing methods and analytical techniques. They perform in-depth analyses of materials and structures to predict behavior and make critical decisions for safety and reliability.
Project Manager: If you’re inclined towards leadership and management, project management roles are within reach. Project managers in NDT oversee inspection projects, ensure timelines are met, and manage teams of NDT professionals.
Advancing to Level 3
NDT Level 3 is the zenith of your NDT journey. At this stage, you become an expert, responsible for procedure development, quality control, and training. By advancing to Level 3, you unlock leadership roles, including:
Quality Control Manager: You oversee NDT operations, ensuring compliance with industry standards and quality control.
Procedure Developer: You create and refine NDT procedures and techniques, ensuring the highest level of accuracy and reliability.
Trainer and Educator: Your knowledge is passed on to the next generation of NDT professionals through training and education.
Industries Hiring NDT Level 2 Inspectors
NDT Level 2 professionals are in demand across a wide spectrum of industries, including:
Aerospace: NDT plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and reliability of aircraft components, from engine parts to airframes.
Oil and Gas: NDT inspectors are essential for maintaining the integrity of pipelines, offshore platforms, and refineries, minimizing the risk of catastrophic failures.
Manufacturing: Quality control is the cornerstone of manufacturing. NDT inspectors validate product quality and safety in sectors like automotive, electronics, and heavy machinery.
Construction: From bridges to skyscrapers, NDT ensures the structural integrity and safety of construction projects.
Nuclear Power: Safety is paramount in the nuclear industry. NDT inspectors play a vital role in monitoring the condition of critical components.
Railways: NDT ensures the safety and reliability of railway systems, from tracks to rolling stock.
Maritime: In shipbuilding and maintenance, NDT inspectors keep vessels seaworthy and safe for navigation.

![BIM Management Course Online [2025] – PGP in Architecture for Global BIM Careers](https://augmintech.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/BIM-Management-Course-Online-2025-–-PGP-in-Architecture-for-Global-BIM-Careers.png)


